Wendepunkte und Krümmung in der Analysis sind zentrale Konzepte, um das Krümmungsverhalten von Funktionen zu bestimmen. Diese Zusammenfassung bietet einen umfassenden Überblick über die Methoden und Mathematik Lösungen zu Wendepunkten.
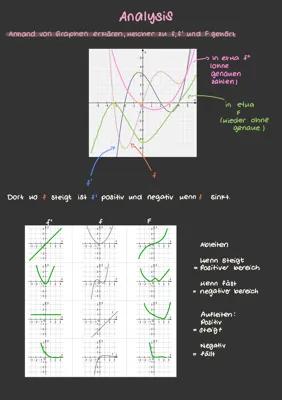
- Die Analyse von Wendepunkten und Krümmung erfolgt durch systematische Schritte, einschließlich der Bestimmung der zweiten Ableitung und Nullstellen.
- Praktische Beispiele demonstrieren die Anwendung dieser Konzepte auf verschiedene Funktionstypen.
- Die Lösung komplexer Aufgaben zeigt, wie man Wendepunkte identifiziert und das Krümmungsverhalten von Funktionen beschreibt.